Stator ventilation duct
QuickField simulation example
The air passes through the stator ventilation duct.
Problem Type
Axisymmetric problem of heat transfer.
Geometry
D = 30 mm, L = 4000 mm.
Given
Air speed in the duct v = 10 m/s,
Duct surface convection coefficient α = 50 W/K-m²,
Pipe thermal load q = 300 W/m².
Task
Determine the air temperature rise along the pipe.
Solution
The pipe is divided into n sections. The heat flux q from each section is calculated. The consumed energy dQ can be found as:
dQ = q·t, where
q - thermal flux (W),
t - duration of air passage through the section, t = (L / n) / v.
Then the air temperature rise is calculated as:
dT = dQ / (dV·C·ρ), where
dQ - consumed energy (J),
dV - volume (m³),
C - thermal capacity of air (J / kg·K),
ρ - density of air (kg/m³).
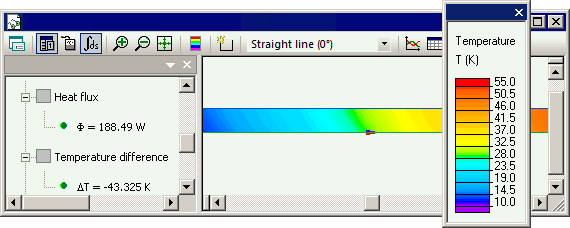
Results
Initial state: air temperature 0°C, thermal flux from the wall to the air q = 18.85 W (per one section), consumed energy dQ = 0.754 J, temperature rize per one section dT = 2.4 °C.
After 3 iterations air temperature rise along the channel is dT = 21.81 °C
* Reference: John H. Lienhard IV, John H. Lienhard V, A heat transfer textbook.
- View simulation report in PDF
- Download simulation files (files may be viewed using any QuickField Edition).